kidney stone treatment image
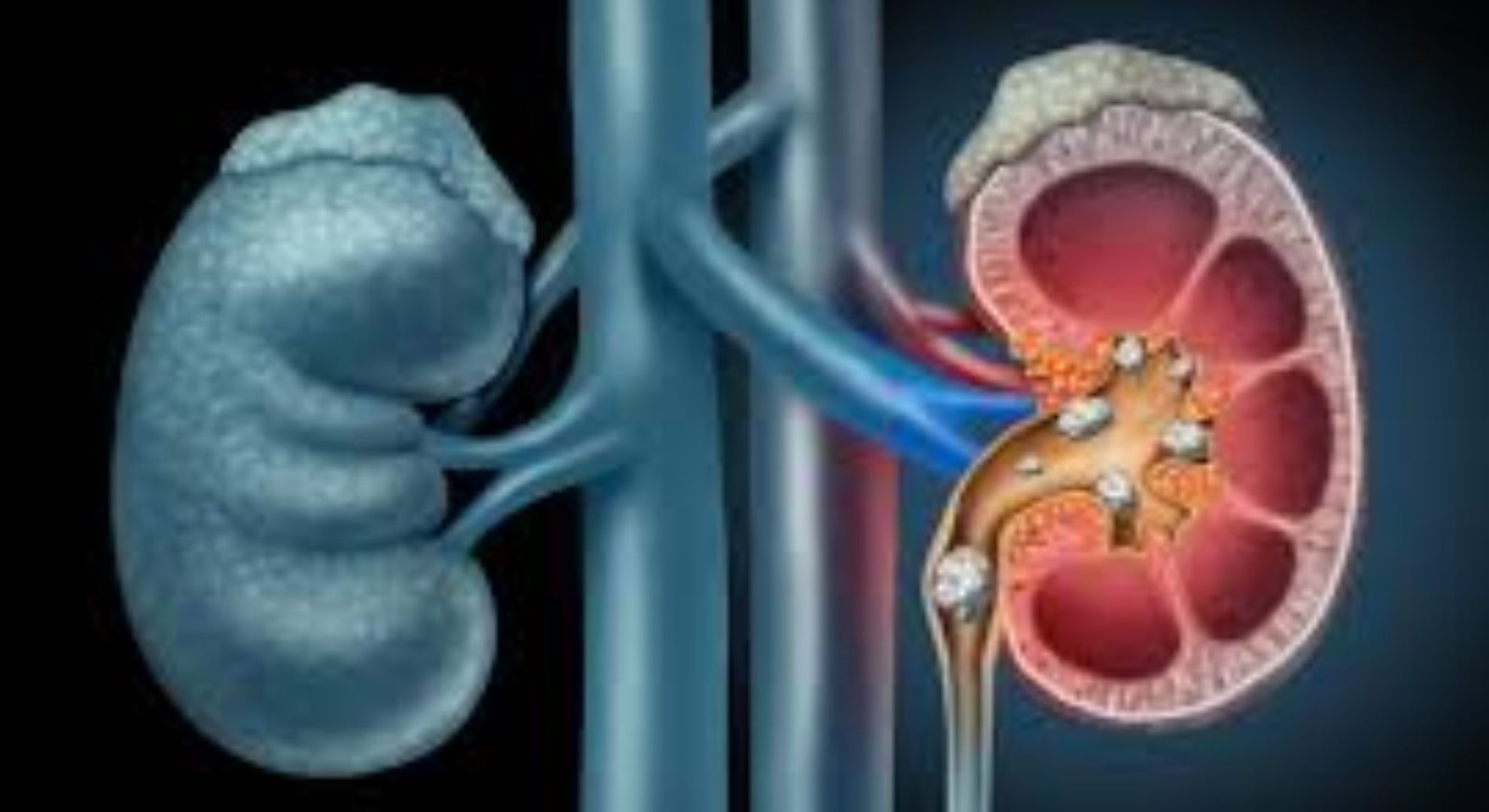
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys and can develop anywhere in your urinary tract. They are a common and painful urologic condition that requires timely intervention. Effective kidney stones treatment depends on understanding how stones form, their type, location, and the symptoms they produce.
In certain cases, procedures like cystolitholapaxy, a minimally invasive method used to break down and remove bladder stones, may be required, especially if the stones are located in the bladder or obstruct the urethra. In rare situations, urethral surgery may be necessary if a stone causes severe blockage or structural complications.
What Are Kidney Stones?
The National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse, National Institutes of Health 2006 What are kidney stones? The stones can be tiny no more than a few grains of sand or as large as a pebble that can obstruct the ureter, the tube that connects the kidney with the bladder, and cause intensely painful spasm.
They form when the urine is too concentrated when it contains more of certain crystal-forming substances than the fluid in the urine can dilute.
Types of Kidney Stones
Understanding the type of stone is essential for effective kidney stones treatment. Common types include:
Calcium Stones: These stones are the most common and are made of calcium oxalate. And this variety can be caused by an excess of oxalate, that is often in some foods and metabolic disorders.
Uric Acid Stones: They form when the urine becomes too acidic. There is, however, an association between a high-purine diet, such as one rich in red meats, organ meats and some kinds of seafood, high uric acid and stone formation.
Struvite Stones: Most often caused by a UTI. Some of these stones might develop very quickly and be very big, big enough to become trapped in the gallbladder without inducing symptoms.
- Cystine Stones: Rare and hereditary, occurring in people with cystinuria, a condition causing excessive cystine in the urine.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are many possible causes of kidney stones, most people have a combination of contributing factors.
Common Causes
- Dehydration: Dehydrated state, as to cause the concentration of urine of stones.
- Diet: Eating foods that are high in oxalate, protein and salt can raise your risk of developing kidney stones.
- Obesity: Risk increases as acid-urine balance moves away from neutral.
- Drugs: Some diuretics, calcium antacids and others.
- Diseases: AWHyperparathyroidism and uric acid stones in the kidney.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Kidney stone symptoms may not appear until the stone moves down the ureters.
Common Symptoms
- Side and back pain (below the ribs) Scream and grunt (very bad signs)
- Pain that radiates down to the lower abdomen and groin
- Fluctuating pain intensity (renal colic)
- Pain during urination
- Hematuria (pink, red or brown urine)
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urination or urgency
- Chills with fever (if there is infection)
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Accurate diagnosis is critical for selecting the right kidney stones treatment approach:
Diagnostic Methods
- Imaging Tests: CT scan, X-ray, ultrasound
- Urinalysis: Checks for blood, crystals, or infection
- Blood Tests: Identify excess calcium or uric acid
- Stone Analysis: Passed stones can be collected and analyzed
Treatment Options for Kidney Stones
For small stones, conservative kidney stones treatment can include:
Home Treatment and Pain Management
For small stones, conservative treatments are often advised:
- More Water Intake: Causes bladder to cleanse out
- Analgesics: Lbuprofen, acetaminophen or naproxen
- Medical Expulsive Therapy: Alpha blockers can relax the muscles of the ureter to help a stone pass through.
Medical Procedures for Larger Stones
If stones are too big to be passed or are causing other complications, more serious treatments are required.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
- It achieves this by breaking the stones up into tiny fragments with sound waves.
- Nonoperative, usually done as an outpatient.
Ureteroscopy
- The bladder and ureter are then accessed with a rigid tube and a telescope, and a laser-tipped tube can be inserted to locate and remove or pulverize the stone.
- Generally used in the lower tract and in stones smaller than 1.5 cm.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
- For larger or complex stones, surgical intervention may be required.
- Suprapubic lithotomy – A small incision is made in the back to reach the stone and remove it.
Open or Robotic Surgery
- Used very infrequently today, it may be performed for exceptionally large stones or anatomic variants.
Prevention of Kidney Stones
It is performed very rarely today and should be reserved only for very large stones or anatomic abnormalities. If you’ve had a kidney stone, your risk of having another goes up. Preventative steps are key.
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
- Drink water: 2.5-3 liters per day
- Consume less sodium: High salt increases calcium in the urine
- Consume fewer oxalate-rich foods: Spinach, nuts, tea
- Consume more calcium: Helps to bind oxalate in the gut. Moderately eat animal protein particularly for uric acid stones. Depending on the type of stone, the doctor may also prescribe medications.
Medications for Prevention
Typically, medications can be prescribed, but depending on the stone medication and pain in coupling:
- Thiazide Diuretics: For calcium stones
- Allopurinol: For uric acid stones
- Potassium Citrate: Contains substance to make urine less acidic
When to See a Doctor
Get emergency medical help if you have:
- Severe or persistent pain
- Blood in urine
- Nausea, vomiting, or fever
- Difficulty urinating or complete blockage
Complications of Untreated Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can cause complications if left untreated:
- Recurrent infections
- Kidney damage or scarring
- Obstruction of urinary flow
- Chronic kidney disease
Conclusion
Kidney stones are also treatable and cause pain. Correct diagnosis, early treatment, hydration and dietary intervention may decrease symptom severity and the recurrence of symptoms. If you believe you are having kidney stones, get to a doctor as soon as you are able, to be diagnosed and receive a natural stone treatment plan.
To read more free article ( Click Here )